Introduction

Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by a collection of symptoms that can vary in intensity, causing discomfort and disruption to daily life. While IBS is not life-threatening, it can significantly impact a person’s overall quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, affected demographics, and various aspects of managing this condition.
How IBS Happens
IBS is a functional disorder, which means that the digestive system appears normal under examination but does not function as it should. The exact mechanisms behind IBS are not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development. These include abnormal muscle contractions in the intestines, heightened sensitivity to pain, and disturbances in the gut-brain axis.
Demographics Affected
IBS can affect people of all ages, but it tends to be more prevalent in young adults, particularly women. It’s estimated that around 10-15% of the global population suffers from IBS at some point in their lives. Individuals with a family history of gastrointestinal issues or those who have experienced traumatic events or high levels of stress are at a higher risk of developing IBS.
Symptoms of IBS
The symptoms of IBS can vary widely from person to person. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal Pain and Discomfort: This is one of the hallmark symptoms of IBS. The pain can be cramp-like, sharp, or dull and is often relieved after a bowel movement.
- Altered Bowel Habits: People with IBS may experience diarrhea, constipation, or a combination of both. Changes in bowel habits can occur over time, alternating between these extremes.
- Bloating and Gas: Excessive gas production and bloating are common complaints among those with IBS.
- Mucus in Stool: Some individuals with IBS may notice an increased presence of mucus in their stool.
- Impact on Quality of Life: IBS can lead to feelings of fatigue, anxiety, and depression, which can further impact a person’s overall well-being.
Lifestyle Considerations
Managing IBS often involves making certain lifestyle adjustments to alleviate symptoms:
- Diet: Identifying trigger foods and avoiding them can help reduce symptoms. Common triggers include high-fat foods, spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and artificial sweeteners.
- Stress Management: Since stress can exacerbate IBS symptoms, practicing stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can be beneficial.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help regulate bowel movements and alleviate stress.
- Adequate Hydration: Drinking enough water can prevent constipation and help maintain digestive regularity.
- Fiber Intake: Gradually increasing fiber intake can aid in managing bowel irregularities. However, excessive fiber intake can worsen symptoms, so moderation is key.
Causes of IBS
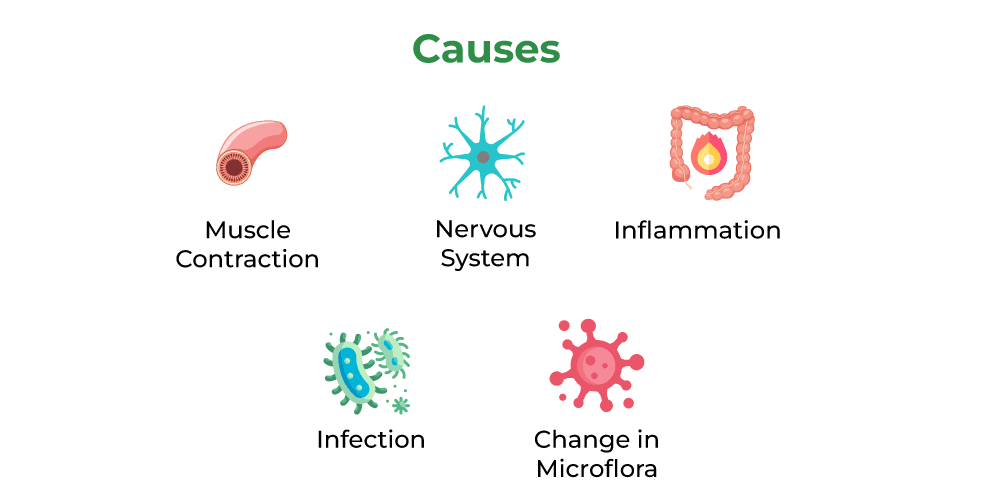
While the exact causes of IBS remain unclear, several factors have been linked to its development:
- Gut-Brain Axis Dysregulation: Communication between the gut and the brain plays a crucial role in digestion. Disruptions in this communication can contribute to IBS symptoms.
- Intestinal Motility: Abnormal muscle contractions in the intestines can lead to irregular bowel movements and discomfort.
- Inflammation: Low-grade inflammation in the intestines may play a role in triggering IBS symptoms.
- Microbiome Imbalance: An imbalance in the gut microbiota has been associated with IBS, suggesting a link between gut health and symptom severity.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment and Management

- Dietary Modifications: Adopting a low-FODMAP (Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols) diet can help alleviate symptoms for some individuals.
- Medications: Over-the-counter medications like antispasmodics, laxatives, and anti-diarrheals can provide temporary relief. Prescription medications may also be recommended by a healthcare provider.
- Counseling and Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychotherapy can be effective in managing stress and its impact on IBS symptoms.
- Probiotics: Some individuals find relief from certain probiotic supplements that promote a healthier gut microbiome.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, hypnotherapy, and herbal remedies have shown promise in alleviating IBS symptoms for some individuals, although more research is needed to establish their efficacy.
Conclusion
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a complex and often challenging condition to manage. Its diverse range of symptoms and potential triggers make a tailored approach essential for effective management. If you suspect you have IBS, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance on suitable treatments and lifestyle adjustments. With the right strategies in place, many individuals with IBS can find relief and regain control over their digestive health and overall well-being.
















Very helpful post about Irritable Bowl Syndrome